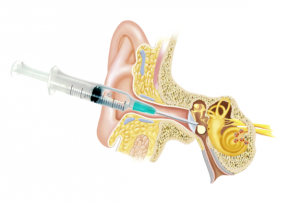
Intratympanic injection of gentamicin for Meniere’s disease
Intra-tympanic gentamicin is used in the treatment of Meniere’s disease.
Gentamicin is an antibiotic that damages the inner ear and the organ of balance when applied behind the eardrum. This treatment can reduce episodes of vertigo in Meniere’s disease.
The intra-tympanic gentamicin is an effective treatment for vertigo in Meniere’s disease, but there is a risk of hearing loss worsening.
Just as in the treatment of sudden hearing loss, at the Polyclinic Centre-Ville, our protocol is to make an intra-tympanic injection per week for three weeks.
The injection is performed using a very fine needle and a microscope. The patient remains lying on a bed for 45 minutes in a private room.
The patient is asked to perform, after a month of the injection of gentamicin, a VNG and a vHIT (balance tests) to look at the percentage of vestibular deficit caused by the injection and to identify the destroyed vestibular canal. The more the deficit is important, the best is the result.
 __________________________
__________________________
Botox® Injection for migraine
Intratympanic injection of cortisone for sudden deafness
Intratympanic injection of gentamicin for Meniere’s disease
Injection of antibiotic or antimycotic in the mastoid cavity
