Intratympanic injection of cortisone for sudden hearing loss
It is indicated especially in cases of sudden hearing loss.
Sudden hearing loss is defined as the occurrence in less than 3 days, of unilateral perception hearing loss in normal eardrum, at least 30 dB in three contiguous frequencies without obvious etiology.
In the case where the oral cortisone treatment did not improve hearing, cortisone may be injected directly into the middle ear through the tympanic membrane in order to increase the concentration of cortisone in the inner ear.
As with systemic corticosteroids (by mouth), the sooner the treatment begins, the chances of recovery of sudden sensorineural hearing loss (perception) are better.
At the Polyclinic Centre-Ville, our protocol is to make an intra-tympanic injection per week for three weeks.
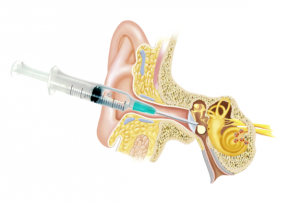
The injection is performed using a very fine needle and a microscope. The patient remains lying on a bed for 45 minutes in a private room.
According to the result of the hearing test conducted one week after the injection, the doctor decides the need to continue or discontinue the injections.
 __________________________
__________________________
Botox® Injection for migraine
Intratympanic injection of cortisone for sudden deafness
Intratympanic injection of gentamicin for Meniere’s disease
Injection of antibiotic or antimycotic in the mastoid cavity
