Ear
Anatomy and function of the ear
Definition
External Otitis
Otitis Media
Retraction Pockets
Cholesteatoma
Myringitis
Mastoiditis
Otosclerosis
Vestibular Schwannoma
__________________________
Anatomy and function of the ear
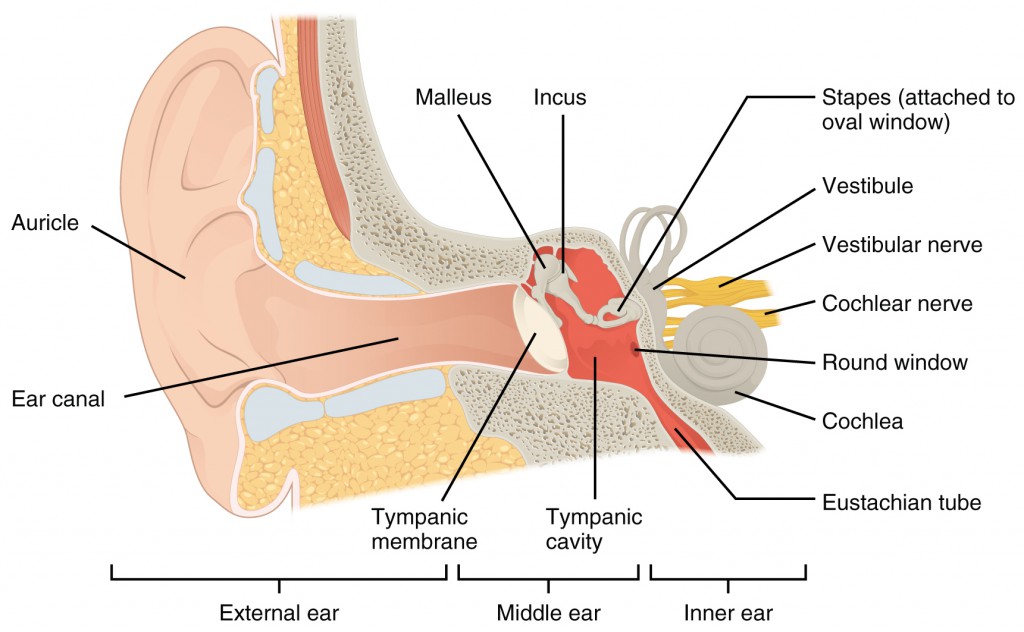
The ear includes the organs of hearing and balance. It is composed of three parts:
The first part is the external ear that includes the auricle, the external auditory canal and the eardrum. The eardrum is similar to a drum skin that vibrates due to the sound waves.
The second part is the middle ear. This cavity contains three tiny bones (malleus, incus and stapes) that transmit sound waves to the inner ear. The Eustachian tube connects the nasopharynx (the posterior portion to the nasal cavity) to the middle ear. This canal allows the aeration of the middle ear and helps to balance the air pressure behind the eardrum.
The deepest portion is the inner ear. The latter is a rigid cavity composed of a dense bone in which is the cochlea and the vestibular system. The cochlea is responsible for transforming the sound wave into electrical current, which is then transmitted to the brain. The vestibular system is responsible for balance. It transmits to the brain and to the eyes information concerning the position and movement of the head.