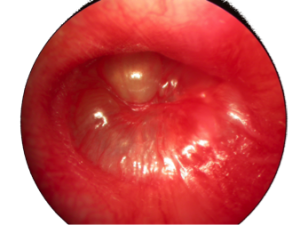
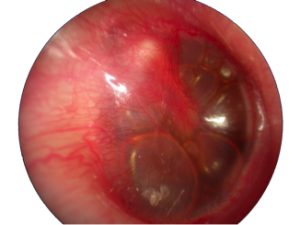
Otitis Media
Acute otitis media is one of the most common infections of childhood. It is usually accompanied by pain, hearing loss and fullness. The presence of fluid in the middle ear with bulging and inflammation of the eardrum is noted. The majority of these infections can be cured without antibiotics. However, antibiotics are necessary for young children or when symptoms persist or are severe.
We must differentiate acute otitis media from serous otitis media. Serous otitis media corresponds to the non-infected fluid of the middle ear. Serous otitis requires no antibiotics. The resolution is spontaneous in most cases. Otherwise, a tube is installed through the eardrum or a subcutaneous tube.
These disturbances are caused by a relative ineffectiveness of the Eustachian tube, a thin canal connecting the middle ear to the back portion of the nose. The trans-tympanic tube has a pressure regulator role of air inside and outside the middle ear. This problem occurs mainly in young children and thankfully it tends to correct when growing up.
Adult and pediatric ENT offer services at the Polyclinique Centre-Ville ORL & Spécialités Médicales. Do not hesitate to ask them. They will be there to explain.
__________________________
Anatomy and function of the ear
Definition
External Otitis
Otitis Media
Retraction Pockets
Cholesteatoma
Myringitis
Mastoiditis
Otosclerosis
Vestibular Schwannoma
