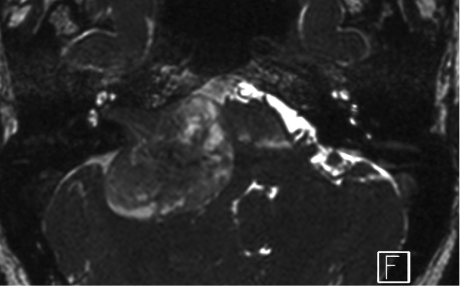
Vestibular schwannoma
The vestibular schwannoma, also called acoustic neuroma, is a benign tumor that develops in the vestibular nerve (balance nerve). It is derived from Schwann cells that are normally found around the vestibular nerve; and hence its name: vestibular schwannoma.
Usually this benign tumor grows slowly (~ 1-2 mm per year). The diagnosis is made through medical magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) requested when an individual refers hearing symptoms affecting only one ear.
Treatment options include observation, radiation therapy and surgical resection. The observation can be considered when the tumor is small and does not progress. Radiation therapy is an option, depending on the choice of the patient, especially when the latter is not a good surgical candidate (secondary to age or other medical problems that would make surgery too risky). Radiation therapy does not remove the tumor, but it prevents the growing up of the tumor. Finally, surgery is the only way to eradicate the tumor. Depending on the size and location of the tumor, some surgical approaches can sometimes allow the preservation of hearing.
__________________________
Anatomy and function of the ear
Definition
External Otitis
Otitis Media
Retraction Pockets
Cholesteatoma
Myringitis
Mastoiditis
Otosclerosis
Vestibular Schwannoma
