Foreign body in the esophagus
Children often choke with coins and small toys while adults rather do with food, such as piece of meat, which remains retained in a pathological site of the esophagus or at the level of a web or stenosis. Immediate surgery is not always necessary in the presence of a foreign body in the esophagus. If the object is soft and not caustic, if ingestion is recent and there are no respiratory symptoms, the patient can sometimes be kept under observation for 24 hours where there would be spontaneous passageway.
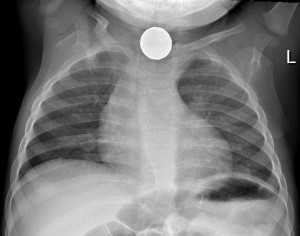
On the other hand, observation is unacceptable in many situations. This approach is acceptable in small children only when there is no doubt the object has already crossed and passed the crico-pharyngeal region. Otherwise, the patient may aspirate the foreign body if it becomes dislodged after coughing, vomiting or dorsal position, then transforming a stable situation to an emergency.
If the patient has respiratory symptoms, removal of the object should be undertaken without delay. In case of hypersalivation, the patient may aspirate secretions. It is therefore prudent to withdraw the object.
 The button battery is a very dangerous foreign body and has to be extracted urgently. Sharp, spiked, irregular or very large objects must also promptly be removed as they may cause perforation of the esophagus. Any foreign body that causes fever, vomiting, incessant nauseating reaction or pronounced discomfort should be the subject of a removal without delay.
The button battery is a very dangerous foreign body and has to be extracted urgently. Sharp, spiked, irregular or very large objects must also promptly be removed as they may cause perforation of the esophagus. Any foreign body that causes fever, vomiting, incessant nauseating reaction or pronounced discomfort should be the subject of a removal without delay.
The observation is not acceptable if the object is in the esophagus for more than 24 hours or for an unknown period. Finally, the observation is not possible in patients with a known anomaly of the esophagus.
Reference: Le Médecin du Québec, Volume 42, Number 5, May 2007.
__________________________
Emergency in ENT
Peritonsillar abscess
Ludwig’s Angina
Foreign body in the ear
Foreign body in the respiratory tract (nose, trachea, bronchi)
Foreign body in the esophagus
Epiglottitis
Epistaxis
Perilymphatic fistula
Nose fracture
Hemorrhage post-adenotonsillectomy
Acute mastoiditis
Facial paralysis
Sudden hearing loss
